Case Study - Chlorinated solvents bioremediation
BIOREMEDIATION STUDY FOR THE REMOVAL OF CHLORINATED SOLVENTS FROM AN ACQUIFER
Matrix
Groundwater
Contaminants
Chlorinated ethenes:
- Tetrachloroethilene PCE
- Trichloroethilene TCE,
- cis-1,2 -Dichloroethene
- 1,1 Dichloroethene
- Vinyl chloride
Proposed Remediation Approach
In situ bioremediation (ISB)
Remedial System
Stimulation of natural occurring microorganism to degrade chloroethene contaminant. Biostimulation involves the delivery of an electron donor into the subsurface.
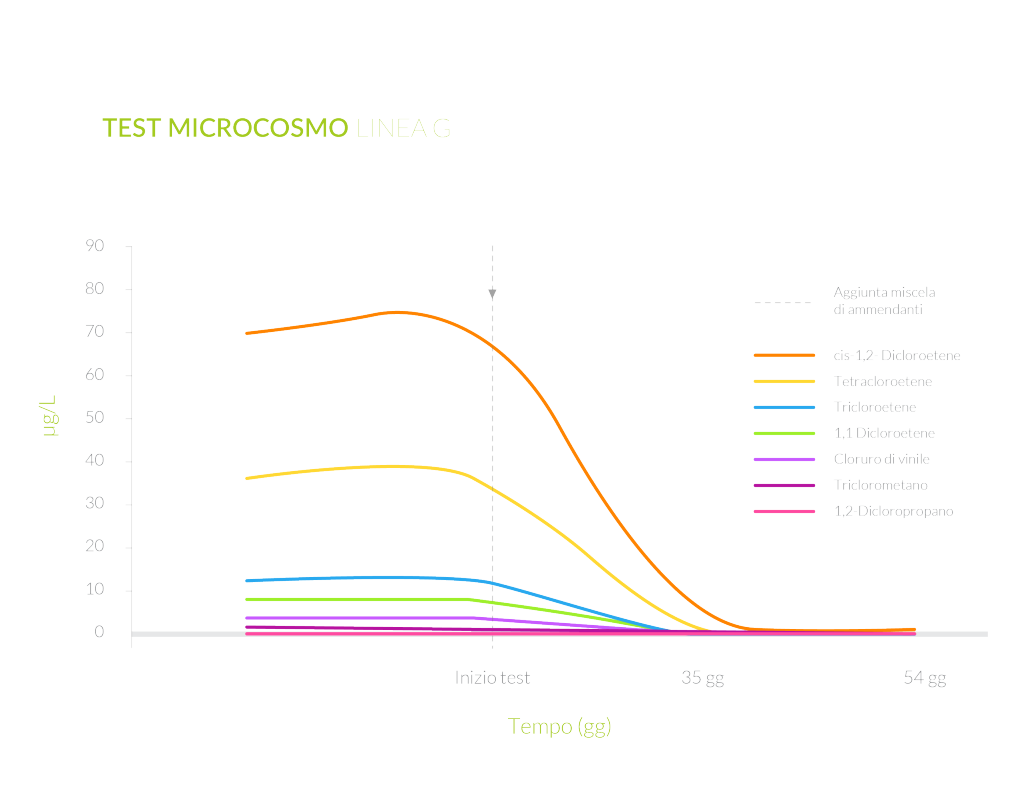
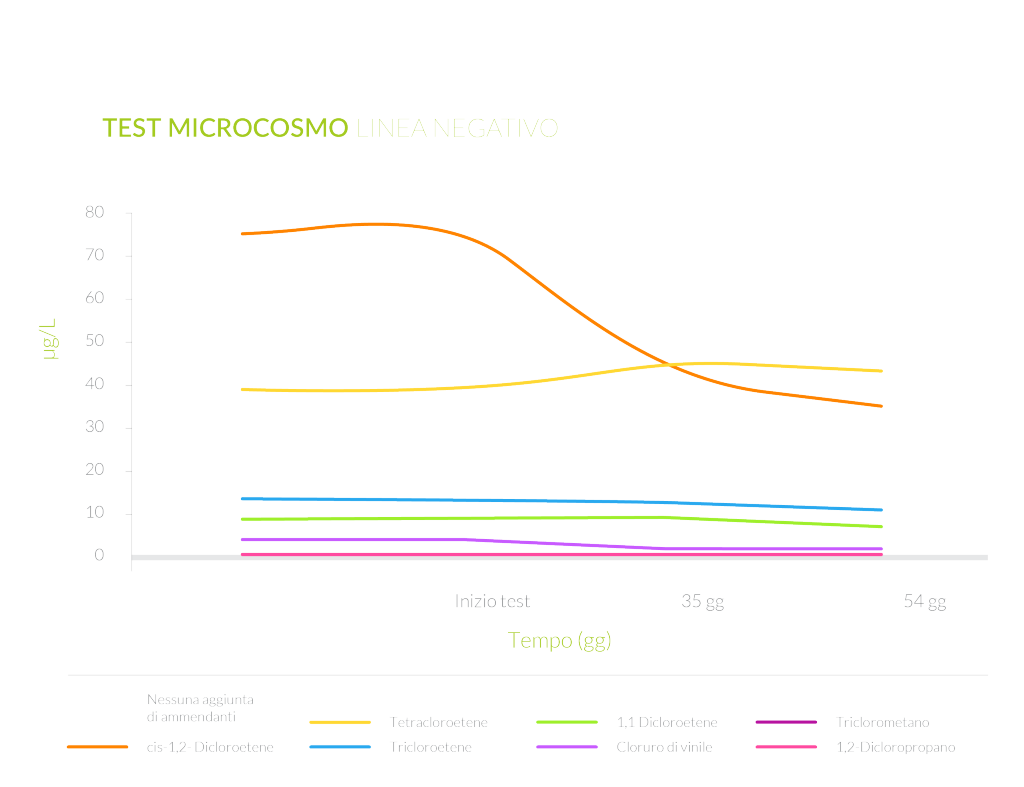
A microcosm test set up at Biosearch Ambiente’s laboratory allowed the determination of the feasibility of a bioremediation approach on a chlorinated solvent impacted groundwater.
Electron donors, as nutrients for the autochthonous microorganism, were added to the contaminated water to stimulate chloroethenes biodegradation.